Configuration
Node Script Execution Guidelines
Important Notice: Avoid executing node scripts with root user privileges. This method is unsupported and could lead to unforeseen complications.
Getting Started:
Obtain the latest script versions from Github.
Tailor the configurations to align with your local setup.
About the Scripts:
OneFinity offers customized scripts aimed at facilitating the node installation process, compatible with Mainnet, Devnet, and Testnet networks, ensuring a broad range of accessibility.
1. Download the OneFinity Scripts
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/onefinity/of-chain-scripts2. Configure the scripts correctly
Setting Up Your Node Environment
To successfully install, upgrade, and manage your node, you'll need to make certain configurations. These involve defining a specific user account, installation directory, and network environment on your system. Let's break down these terms:
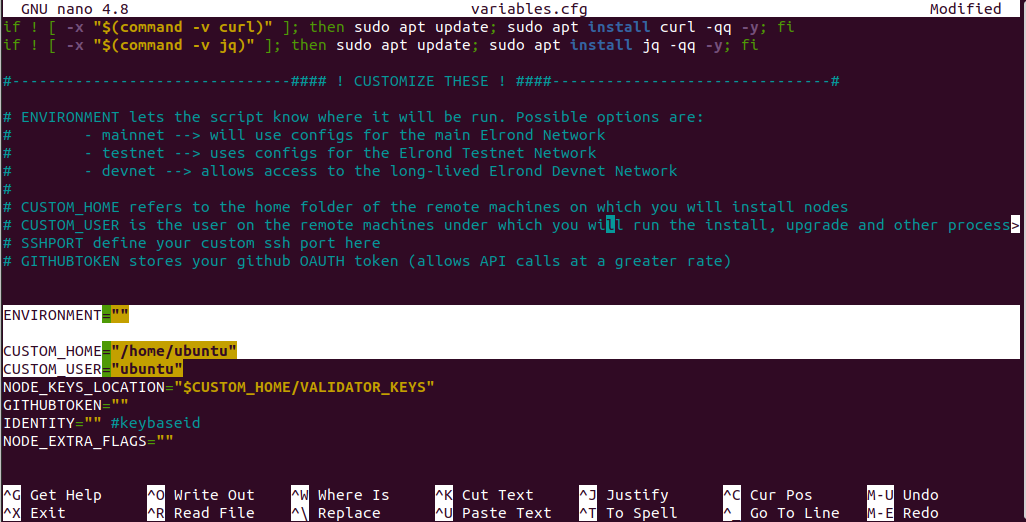
CUSTOM_USER: The username on your computer that will be used for running the installation and other related processes.CUSTOM_HOME: The directory where your node will be installed.ENVIRONMENT: Specifies the OneFinity network you intend to connect to. This can bemainnet,testnet, ordevnet.
Before proceeding, you'll need to update the variables.cfg file to include the necessary details, primarily your username. Here's how to find and set it:
Finding Your Username
Your system's username is crucial for the setup. If you're uncertain of your username, you can quickly find it by executing the following command in your terminal:
This command will display your current username. Remember to accurately record this as it will be crucial for the script configurations to function properly, this will be your CUSTOM_USER.
Configuring the Script
After obtaining your username, open variables.cfg and update the placeholders (CUSTOM_USER, CUSTOM_HOME, ENVIRONMENT) with your actual user information. This is crucial for your node's functionality.
To open the variables.cfg file in the nano editor, use the following command:
Change the variables ENVIRONMENT, CUSTOM_HOME and CUSTOM_USER as highlighted in the image below:
To save and exit in vi or vim: Press Shift+Z twice.
In nano: Press Ctrl+X, then Y, and
Grants elevated privileges
To enable sudo commands for your user without requiring a password, follow these steps:
Open Terminal.
Type
sudo visudo -f /etc/sudoers.d/myOverridesand press Enter. This will allow you to edit the sudoers file securely.Once the file is open in the editor, navigate to the end by pressing
Shift + G.Press
oto start a new line. Then, enter the following line, replacingyourusernamewith your actual username (you can find your username by runningwhoami):To save and exit, press
Esc, thenShift + ZZ(hold downShiftand pressZtwice).
This configuration will enable your user to execute sudo commands without prompting for a password. Ensure you replace yourusername with the correct username. Proceed with caution, as this operation grants elevated privileges.
Last updated